The Science of LED Light Therapy: How it Rejuvenates the Skin
What is LED Light Therapy?
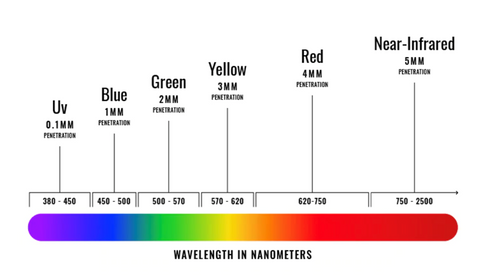
Understanding Wavelengths and Their Role in LED Therapy

- Boosts Collagen Production: More collagen means fewer fine lines and wrinkles. Over time, regular red light treatments can lead to visibly plumper and smoother skin.
- Enhances Circulation: Red light therapy promotes blood flow, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to the skin. This can result in a healthy, radiant glow.
- Reduces Inflammation: It has powerful anti-inflammatory properties, making it ideal for soothing irritated or inflamed skin, including conditions like rosacea.
Red light has been extensively studied for its regenerative properties. One study published in The Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy found that red light therapy significantly improved the skin’s appearance in participants who received regular treatments over 12 weeks. Another research conducted by The American Academy of Dermatology reported that red light at 660nm increases the skin’s healing process, accelerating cell turnover and collagen remodeling.
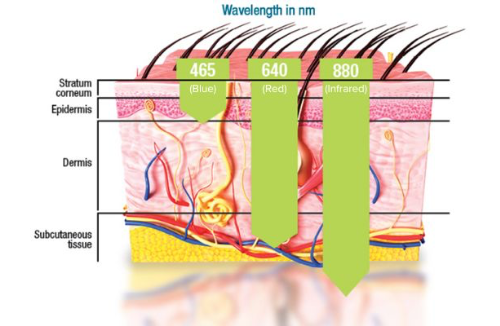
How LED Light Therapy Rejuvenates the Skin
Blue Light Therapy (400-495nm): The Acne Fighter
- Kills Acne-Causing Bacteria: Blue light directly targets Propionibacterium acnes, the bacteria responsible for inflammatory acne, reducing the severity and frequency of breakouts.
- Regulates Sebum Production: Blue light can also help balance oil production in the skin, which can prevent clogged pores that often lead to acne.
- Reduces Inflammation: Just like red light, blue light has anti-inflammatory effects, which is particularly beneficial for acne-prone skin.
A clinical study in The Journal of Dermatological Science demonstrated that blue light therapy significantly reduced inflammatory acne lesions after several weeks of treatment. It was found to be particularly effective when combined with red light therapy, creating a powerful acne-fighting duo that targets both the surface bacteria and deeper skin repair processes.

Green Light (495–570 nm) for Pigmentation
- Reduces Hyperpigmentation: Green light helps break down clusters of melanin (pigment), reducing the appearance of dark spots and discoloration.
- Brightens Skin: By inhibiting melanin overproduction, green light can create a more luminous, even skin tone.
- Calms the Skin: This wavelength has a calming effect on the skin, reducing redness and promoting an overall sense of calm.
According to research published in The Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, green light therapy has shown promising results in reducing pigmentation when used consistently. By targeting the melanocytes (cells that produce pigment), green light helps to diminish existing spots while preventing new ones from forming.
Near-Infrared Light (700–1200 nm) for Healing
How Often Should You Get LED Light Therapy?
To Schedule Your LED Facial at Anita’s Skincare Clinic
Reap the Benefits of LED Therapy with a Skincare Consultation
References:
- “LED Phototherapy: A Review of the Literature,” The Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy. Study on red light therapy and its effects on collagen production. [Accessed from Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy].
- “Acne Treatment with Blue Light: The Efficacy of Blue LED Therapy on Acne Vulgaris,” Journal of Dermatological Science. Study on the effects of blue light therapy in reducing acne lesions. [Accessed from Journal of Dermatological Science].
- “The Effects of Red and Blue Light on Inflammatory Skin Diseases: A Comprehensive Review,” American Academy of Dermatology. Overview of red and blue light therapy for acne and inflammation. [Accessed from American Academy of Dermatology].
- “Green LED Phototherapy for the Treatment of Hyperpigmentation,” Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. Study on green light’s impact on pigmentation and melanin production. [Accessed from Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology].
- “Near-Infrared Light Therapy: A Powerful Tool for Anti-Aging and Healing,” Photomedicine and Laser Surgery. Research on near-infrared therapy’s effects on tissue repair and deep skin healing. [Accessed from Photomedicine and Laser Surgery].


